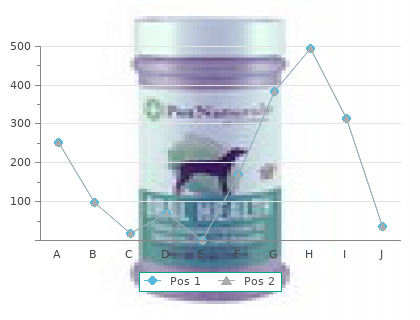

ECOSHELTA has long been part of the sustainable building revolution and makes high quality architect designed, environmentally minimal impact, prefabricated, modular buildings, using latest technologies. Our state of the art building system has been used for cabins, houses, studios, eco-tourism accommodation and villages. We make beautiful spaces, the applications are endless, the potential exciting.
2018, Air Force Institute of Technology, Cole's review: "Norvasc generic (Amlodipine) 10 mg, 5 mg, 2.5 mg. Order Norvasc online.".
Upledger coined the term craniosacral therapy purchase norvasc 5 mg otc blood pressure jumps up and down, which refers to a form of therapeutic manipulation that is oriented to tissue buy discount norvasc 5 mg on-line zofran arrhythmia, fluid, membranes and energy. Craniosacral therapy practitioners touch areas of the patient lightly to sense the cranial rhythm impulse of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), said to be similar to feeling the pulse of blood vessels. Practitioners then use subtle manipulations over the skull and other areas with the aim of restoring balance by removing restrictions to CSF movement, a process that is proposed to help the body heal itself and improve a wide range of conditions. Treatment sessions usually last between 30 and 60 minutes. There are numerous anecdotes about treatment benefits, although effectiveness and safety have not been thoroughly studied scientifically. Craniosacral therapy may be practiced by osteopathic doctors, chiropractors, naturopathic doctors or massage therapists. This technique is sometimes referred to as cranio-occipital technique or cranial osteopathy (when practiced by osteopathic doctors), although it is controversial whether there are subtle differences between these approaches. Scientists have studied craniosacral therapy for the following health problems:Early evidence shows that craniosacral therapy does not appear to have an effect on heart or breathing rates. More information is needed before a conclusion can be drawn. Preliminary research shows that there is no added benefit for using craniosacral therapy during labor and delivery. Check with a qualified obstetrician before using craniosacral therapy. Craniosacral therapy has been suggested for many uses, based on tradition or on scientific theories. However, these uses have not been thoroughly studied in humans, and there is limited scientific evidence about safety or effectiveness. Some of these suggested uses are for conditions that are potentially life-threatening. Consult with a health care provider before using craniosacral therapy for any use. Although the movements of this technique are usually gentle, there may be a small risk of stroke, nervous system damage, bleeding in the head, intracranial aneurysm or increased pressure in the brain. The following people should approach craniosacral therapy with caution: those with recent head trauma or skull fracture, those with diseases that affect the brain or spinal cord, those with conditions in which a change in pressure in the brain would be dangerous, and those with disorders of blood clotting. In theory, craniosacral therapy may make some existing symptoms worse. Adverse results have been reported in patients with traumatic brain syndrome. There are anecdotal reports of diarrhea, headache and increased anger after treatment. It has been proposed that craniosacral therapy may enhance the effects of drugs used for diabetes, epilepsy or psychiatric disorders, although this has not been tested in scientific studies. Craniosacral therapy should not be relied on as the sole treatment (instead of more proven approaches) for potentially severe conditions, and it should not delay consultation with an appropriate health care provider about a symptom or condition. Craniosacral therapy has been suggested for many conditions. There are numerous anecdotes about successful treatment with craniosacral therapy, although effectiveness and safety have not been thoroughly tested scientifically. Speak with your health care provider if you are considering treatment with craniosacral therapy. The information in this monograph was prepared by the professional staff at Natural Standard, based on thorough systematic review of scientific evidence. The material was reviewed by the Faculty of the Harvard Medical School with final editing approved by Natural Standard. Natural Standard reviewed more than 30 articles to prepare the professional monograph from which this version was created.
Furthermore buy generic norvasc 2.5 mg blood pressure medication every other day, discontinuation or dose reduction of rosiglitazone must be considered [see Boxed Warning ] discount 10 mg norvasc with mastercard hypertension and kidney disease. Patients with congestive heart failure (CHF) NYHA Class I and II treated with rosiglitazone have an increased risk of cardiovascular events. A 52-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled echocardiographic study was conducted in 224 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and NYHA Class I or II CHF (ejection fraction ?-T45%) on background antidiabetic and CHF therapy. An independent committee conducted a blinded evaluation of fluid-related events (including congestive heart failure) and cardiovascular hospitalizations according to predefined criteria (adjudication). Separate from the adjudication, other cardiovascular adverse events were reported by investigators. Although no treatment difference in change from baseline of ejection fractions was observed, more cardiovascular adverse events were observed with rosiglitazone treatment compared to placebo during the 52-week study. Emergent Cardiovascular Adverse Events in Patients With Congestive Heart Failure (NYHA Class I and II) Treated With Rosiglitazone or Placebo (in Addition to Background Antidiabetic and CHF Therapy)- with overnight hospitalization- without overnight hospitalizationNew or worsening dyspneaIncreases in CHF medicationCardiovascular hospitalization *Investigator-reported, non-adjudicatedIschemic adverse eventsInitiation of Avandaryl in patients with established NYHA Class III or IV heart failure is contraindicated. Avandaryl is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure. In view of the potential for development of heart failure in patients having an acute coronary event, initiation of Avandaryl is not recommended for patients experiencing an acute coronary event, and discontinuation of Avandaryl during this acute phase should be considered. Patients with NYHA Class III and IV cardiac status (with or without CHF) have not been studied in controlled clinical trials. Avandaryl is not recommended in patients with NYHA Class III and IV cardiac status. Meta-Analysis of Myocardial Ischemia in a Group of 42 Clinical Trials: A meta-analysis was conducted retrospectively to assess cardiovascular adverse events reported across 42 double-blind, randomized, controlled clinical trials (mean duration 6 months). Some trials were placebo-controlled and some used active oral antidiabetic drugs as controls. Placebo-controlled studies included monotherapy trials (monotherapy with rosiglitazone versus placebo monotherapy) and add-on trials (rosiglitazone or placebo, added to sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin). Active control studies included monotherapy trials (monotherapy with rosiglitazone versus sulfonylurea or metformin monotherapy) and add-on trials (rosiglitazone plus sulfonylurea or rosiglitazone plus metformin, versus sulfonylurea plus metformin). A total of 14,237 patients were included (8,604 in treatment groups containing rosiglitazone, 5,633 in comparator groups), with 4,143 patient-years of exposure to rosiglitazone and 2,675 patient-years of exposure to comparator. Myocardial ischemic events included angina pectoris, angina pectoris aggravated, unstable angina, cardiac arrest, chest pain, coronary artery occlusion, dyspnea, myocardial infarction, coronary thrombosis, myocardial ischemia, coronary artery disease, and coronary artery disorder. In this analysis, an increased risk of myocardial ischemia with rosiglitazone versus pooled comparators was observed (2% rosiglitazone versus 1. An increased risk of myocardial ischemic events with rosiglitazone was observed in the placebo-controlled studies, but not in the active-controlled studies. This increased risk reflects a difference of 3 events per 100 patient-years (95% CI -0. Forest Plot of Odds Ratios (95% Confidence Intervals) for Myocardial Ischemic Events in the Meta-Analysis of 42 Clinical TrialsA greater increased risk of myocardial ischemia was also observed in patients who received rosiglitazone and background nitrate therapy. For rosiglitazone (N = 361) versus control (N = 244) in nitrate users, the odds ratio was 2. This increased risk represents a difference of 12 myocardial ischemic events per 100 patient-years (95% CI 3. Most of the nitrate users had established coronary heart disease. Among patients with known coronary heart disease who were not on nitrate therapy, an increased risk of myocardial ischemic events for rosiglitazone versus comparator was not demonstrated. Myocardial Ischemic Events in Large, Long-Term, Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Trials of Rosiglitazone: Data from 3 other large, long-term, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trials of rosiglitazone were assessed separately from the meta-analysis. These 3 trials include a total of 14,067 patients (treatment groups containing rosiglitazone N = 6,311, comparator groups N = 7,756), with patient-year exposure of 21,803 patient-years for rosiglitazone and 25,998 patient-years for comparator. Duration of follow-up exceeded 3 years in each study. ADOPT (A Diabetes Outcomes Progression Trial) was a 4- to 6-year randomized, active-controlled study in recently diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes nas_ve to drug therapy. It was an efficacy and general safety trial that was designed to examine the durability of rosiglitazone as monotherapy (N = 1,456) for glycemic control in type 2 diabetes, with comparator arms of sulfonylurea monotherapy (N = 1,441) and metformin monotherapy (N = 1,454).
The definition of drug addiction refers to the obsessive and repeated use of dangerous amounts of drugs and the appearance of withdrawal symptoms when not using drugs cheap 2.5 mg norvasc arrhythmia from clonidine. The effects of drug addiction seen generic norvasc 2.5mg without prescription arrhythmia flowchart, due to this compulsion, are wide-ranging and profound. Effects of drug addiction are felt by the addict both physically and psychologically. The effects are also seen in those around the addict, like family members. The effects of drug addiction also include the cost to the justice and health care systems. Violent behavior is most closely tied to alcohol use and alcohol abuse is responsible for the disability of 58. It was estimated the effects of drug addiction cost the U. This number represents health care expenses, lost wages, prevention program costs and criminal justice system costs, among others. The psychological effects of drug addiction come from the reason the user is addicted to drugs, as well as the changes that take place in the brain once a person becomes a drug addict. Initially, many people start using drugs to cope with stress or pain (read about: what causes drug addiction ) An effect of drug addiction is creation of a cycle where anytime the user encounters stress or pain, they feel the need to use the drug. This is one of the psychological effects of drug addiction involved in "craving" of the drug. Craving is an effect of drug addiction whereby the addict is obsessed with obtaining and using the drug, to the exclusion of all else. One of the psychological effects of addiction involved in craving is the belief the addict cannot function or handle life without use of the drug. Some of the primary physical effects of drug addiction take place in the brain. Drug addiction changes the way the brain functions and impacts how the body perceives pleasure. These effects of drug addiction are because the drug repeatedly floods the brain with the chemicals dopamine and serotonin during drug use. The brain adapts and comes to expect, and depend on, these drug-induces highs. Physical effects of drug addiction are also seen in babies of drug abusers as well as in mortality statistics. One effect of drug addiction is: children born to drug-using mothers can be cognitively affected throughout life. Regarding mortality, one-in-four deaths are due to the effects of drug addiction. However, there is no need to let an addiction progress to this point. There are several ways of getting and providing drug addiction help for yourself or someone else. Drug addiction help should be accessed medically through a clinic, emergency room or doctor. Once initial medical help with drug addiction is given, referral to a treatment program or other resources is critical. The referral must be followed up and any medications ordered by the doctor must be taken as prescribed. Then help for drug addiction will come from the treatment program itself. Treatment programs typically include access to medical personnel, as well as counselors and other addiction treatment specialists to further provide help with drug addiction. Drug addiction help may not be wanted by the drug addict, even if it is needed. In an emergency, help with drug addiction should always be given by a medical professional. Any time an overdose is suspected or the person loses consciousness, has seizures or drastic changes in vital signs, help with drug addiction means calling 9-1-1 immediately.