
ECOSHELTA has long been part of the sustainable building revolution and makes high quality architect designed, environmentally minimal impact, prefabricated, modular buildings, using latest technologies. Our state of the art building system has been used for cabins, houses, studios, eco-tourism accommodation and villages. We make beautiful spaces, the applications are endless, the potential exciting.
2018, Methodist College, Pakwan's review: "Sinequan generic (Doxepin) 75 mg, 25 mg, 10 mg. Safe Sinequan online no RX.".
For example buy 75 mg sinequan visa anxiety symptoms tight chest, RBC storage studies essentially marinated in a bath of ever-increasing waste products routinely measure rheological properties of RBCs purchase sinequan 75mg on line anxiety symptoms bloating, some RBC (eg, lactate). What seems clear is that storage is a distinctly surface molecules, and RBC metabolism (including 2,3-DPG levels unnatural state to which we expose blood cells for various periods of that regulate oxygen affinity curves). The overall issue breaks down to 2 major questions: (1) to lecular changes have been described that may diminish an RBC’s what extent do stored blood cells maintain their desired function and ability to deliver oxygen to tissues, not only through oxygen therefore constitute an efficacious product? Although the above questions are conceptually simple and straight- There is a strong argument to be made that stored RBCs have forward, generating meaningful answers is a considerable challenge 2-4 decreased function after transfusion. Some have even expressed with which the field of transfusion medicine has been wrestling. This extreme view appears to be lack of optimal assays and thus the inability to observe certain contradicted by the observation that patients who are severely biologies, substantial donor-to-donor differences in blood storage, anemic and symptomatically hypoxic improve clinically after and the wide variety of disorders for which transfusion is given. Similarly, some patients undergo massive transfusion This landscape renders the question “is stored blood efficacious? The observation that such patients live indicates that not easily be generated. However, breaking down the question into stored RBCs do have at least some function posttransfusion. Finally, more focused inquiries regarding subsets of patients and categories chronically anemic patients and those requiring hematological of blood aging may allow a more accurate analysis. However, such observations Is stored blood efficacious? It is also worth solutions are approved, which are the same criteria that are noting that even if the transfused blood cells were functioning generally used in clinical research, do not measure the function of optimally, this does not necessitate that transfusions would have a Hematology 2013 651 Table 1. Ongoing randomized controlled trials testing effects of RBCs stored for longer versus shorter periods of time Old blood Young Primary outcomes Trial name group blood group Patient population measured Status Red Cell Storage Duration Study 21 d or more 10 d or fewer Complex cardiac surgery Multiple organ dysfunction Under way (RECESS) patients score Age of Blood Evaluation (ABLE) Standard issue 7 d or fewer Critically ill adults 90-day mortality (all cause) Under way and morbidity Age of Red Blood Cells in 14. In aggregate, it seems that current storage technologies allow the Biological changes during RBC storage transfusion of blood cells that retain some of their native function. Although the potential toxicities and sequelae of transfused RBCs That having been noted, it is likewise true that the current metrics by remain controversial, it has been unequivocally demonstrated that a which we measure RBC storage quality do not include the ability to distinct series of biochemical changes occur during storage that deliver oxygen or regulate vascular tone. Rather, circulation (with- gives rise to a litany of chemical and cellular entities known to have out any measure of function) is the current in vivo criterion that is biological activities in other contexts. Therefore, as ongoing efforts are made to characterize and that such entities will have effects upon transfusion recipients. Of improve blood storage conditions, the field must remain mindful course, reason does not always predict what is empirically observed, of the disconnect between what is measured as metrics of quality but the extensive experimental evidence on these changes is one and the in vivo function that we are seeking to introduce with driving force behind the strength of opinion that stored RBCs are transfusion. These substances can be divided into several different categories. Several highly provocative retrospective studies have reported that Effectors of vascular tone transfusing older RBC units results in significantly worse medical Free hemoglobin (from in-bag hemolysis) can scavenge NO, which outcomes compared with transfusing fresher RBC units. However, may increase vascular tone by depriving blood vessels of the NO required to relax appropriately. In addition to NO sufficiently conflicting and the independent studies so variant in approach so as to preclude formal meta-analysis. In this context, it has been It has been reported in both mice and dogs that transfusion of stored argued that the statistical power of the ongoing prospective trials, (but not fresh) RBCs results in recipients having systemic inflamma- while sufficient to test larger effects, may miss smaller differences tory cytokine release. The field is eagerly controlled trial in healthy volunteers showed no induction of awaiting the outcome of the ongoing trials. However, due to the standard practice of giving data raise the possibility that human biology simply differs from fresher blood to neonates, the mean age of RBCs in the “fresh” and murine and canine biology in this regard. Therefore, it consistent with the data are the hypotheses that multiple units must is unclear whether ARIPI had a group with old enough RBCs to test be given and that the effect would be augmented in sick patients the hypothesis in a broader context. However, what is clear is that in with baseline innate immune activation. Recent studies lend some 652 American Society of Hematology support to this latter notion in patients experiencing trauma. Therefore, the very general hypothesis that “older blood results in after transfusion in neonates, although fresh RBCs were not worse medical outcomes” covers the essence of what one would compared with older RBCs in that study. However, the more generalized a hypothesis, the more one into a pediatric population, with less induction from washed units. The result can lead to questions that are essentially meaningless in substance and impos- In addition to inducing cytokines in mice and dogs, transfusion of sible to answer. Although it is not clear that this is the case with older units of RBCs resulted in plasma factors that support the testing the hypothesis that “older blood results in worse medical growth of ferrophilic bacteria in either mice or human speci- outcomes,” it is necessary to give careful attention to this issue and mens.
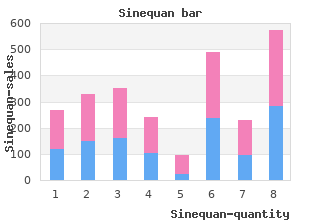
The chance of live birth did not pregnancy outcome than starting it once pregnancy is established discount sinequan 75 mg mastercard anxiety x blood and bone. Based on the available evidence that also included trials comparing 2 active treatments generic sinequan 10 mg fast delivery anxiety disorder 3000,28 Aspirin to prevent preeclampsia various guidelines recommend against the use of antithrombotic A meta-analysis of individual patient data from 31 randomized agents in women with unexplained recurrent pregnancy loss. How I treat women with aspirin or LMWH to prevent pregnancy complications My approach in most patients My alternatives (not exhaustive) Recurrent pregnancy loss (2 or more), No LMWH, no aspirin unexplained Recurrent pregnancy loss (3 or more) and Aspirin 80 mg preconceptionally Start aspirin as soon as a pregnancy test is APS positive (Low-dose) LMWH as soon as a pregnancy In case of a history of venous or arterial test is positive thromboembolism and long term use of anticoagulant therapy; therapeutic dose LMWH and no aspirin In case of a history of a single episode of venous thromboembolism, antepartum and postpartum LMWH according to current guidelines and no aspirin24 Recurrent pregnancy loss (2 or more) and Enroll in ALIFE2 trial after informed In case of a history of venous or arterial inherited thrombophilia consent, and randomize to either LMWH thromboembolism and long term use of or no LMWH anticoagulant therapy; therapeutic dose LMWH and no aspirin If no informed consent for trial participation, In case of a history of a single episode of venous no LMWH thromboembolism, antepartum and No aspirin postpartum LMWH according to current guidelines24 History of severe preeclampsia, unexplained Counsel about the modest risk reduction of aspirin and prescribe on an individual basis No LMWH History of severe preeclampsia, a single late Aspirin 80 mg as soon as a pregnancy test Start aspirin in the second trimester pregnancy loss, placental abruption, or is positive severe intra-uterine growth restriction and (Low dose) LMWH as soon as a pregnancy In case of a history of venous or arterial APS test is positive thromboembolism and long term use of anticoagulant therapy; therapeutic dose LMWH added to aspirin In case of a history of a single episode of venous thromboembolism, antepartum and postpartum LMWH according to current guidelines added to aspirin24 History of severe preeclampsia and Counsel about the modest risk reduction of In case of a history of venous or arterial inherited thrombophilia aspirin and prescribe on an individual thromboembolism and long term use of basis anticoagulant therapy; therapeutic dose LMWH and no aspirin No LMWH In case of a history of a single episode of venous thromboembolism, antepartum and postpartum LMWH according to current guidelines24 History of a single late pregnancy loss, No LMWH In case of a history of venous or arterial placental abruption or severe intra-uterine thromboembolism and long term use of growth restriction and inherited anticoagulant therapy; therapeutic dose thrombophilia LMWH and no aspirin In case of a history of a single episode of venous thromboembolism, antepartum and postpartum LMWH according to current guidelines24 Forjustification,pleaseseefulltext. In a few small studies, the use of LMWH and with aspirin only (n 109; RR 0. Comparing any heparin (unfractionated observed a profound effect of unfractionated heparin added to heparin or LMWH) combined with aspirin (n 199) with aspirin aspirin; this is markedly lower than in the comparator arms of only (n 199), the beneficial effect of heparin of reducing the risk studies comparing LMWH and aspirin with aspirin only or aspirin 396 American Society of Hematology with placebo, in which the chances of a live birth varied between study, a nonsignificant increase in live birth was observed in the 2 68% and 80%. This indicates clinical heterogeneity between the active treatment arms for women with inherited thrombophilia (RR trials. We are currently performing the observed (RR for live birth for women treated with bemiparin ALIFE2 study (NTR 3361; www. The ACCP guidelines recommend unfractionated hepa- pregnancy surveillance only. The Royal College of without aspirin compared with no treatment in women with a history Obstetricians and Gynaecologists guidelines state that pregnant of various pregnancy complications, including preeclampsia, small- women with APS should be considered for treatment with aspirin for-gestational age babies, and placental abruption, to reduce the combined with heparin to prevent further miscarriage, without 29 risk of recurrence in subsequent pregnancies. These 6 studies were specifying clinical criteria of APS in the recommendation. The primary outcome was a composite of preeclampsia, birth of a small-for-gestational- Therefore, although evidence for a beneficial effect of heparin th age newborn ( 10 percentile), placental abruption, or pregnancy combined with aspirin in women with APS and 3 or more loss later than 20 weeks. The effect of antithrombotic agents in mediated pregnancy complications, compared with 127 of 296 different subgroups of women with APS based on laboratory or (42. Nevertheless, based on the currently available evidence thrombophilia. Although the pooled risk reduction is statistically of studies with small numbers of participants, clinicians worldwide significant, the results are strikingly positive in some studies, with have adopted the practice of prescribing aspirin with or without 36-39 relative risk reductions up to 85%, whereas in the 2 most heparin to all women with APS. This is reflected by the statistical heterogeneity that no sufficiently sized trials have been performed that show an effect 2 17 was also observed in the meta-analysis (I 69%). In all studies of heparin on the prognosis of a subsequent pregnancy. The combined, 25% of women had thrombophilia and only the FRUIT Habenox trial randomized women with at least 3 consecutive first 40 study was dedicated to thrombophilic women only. In this trial, trimester miscarriages to enoxaparin 40 mg and placebo once daily women with inherited thrombophilia and a history of preeclampsia (n 68), enoxaparin 40 mg and aspirin 100 mg (n 63), or aspirin th 33 or intrauterine growth restriction, 10 percentile requiring deliv- 100 mg (n 76); there was no control group without intervention. The primary outcomes were recurrence of a hyperten- 0. Almost a quarter of the included women gestation or recurrence at any gestational age. The overall primary had either hereditary thrombophilia or anticardiolipin antibodies outcome did not differ between the 2 groups; hypertensive disorders 40 GPL or beta 2 glycoprotein I antibodies, and no differential occurred in 18. None of the women in after 10 weeks gestation and heterozygous factor V Leiden muta- the LMWH aspirin group developed recurrent hypertensive disor- tion, prothrombin G20210A mutation, or protein S deficiency; they ders before 34 weeks gestational age, whereas 6 (8. Women treated with enoxaparin had a much development of recurrent hypertensive disorders, with 3 women higher chance of a live birth than those allocated to aspirin (86% and delivering at 19-22 weeks (risk difference 8. The recently finished TIPPS study, which included 95% CI 7–34). However, several methodological issues were thrombophilic women either at high risk for pregnancy-mediated raised, and the results of this single study have not been confirmed complications or at high risk of pregnancy-related venous thrombo- by other trials; therefore, this regimen was not endorsed by the embolism, randomized women between LMWH and no LMWH and ACCP guidelines for women with a single previous pregnancy loss 42 24,35 found no effect of the intervention. In the SPIN and ALIFE studies, small proportions of the study Why should we prescribe prudently? In the ALIFE reactions such as itching and swelling, and the rarer complications Hematology 2014 397 of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia and heparin-induced osteope- the Confidential Enquiries into Maternal Deaths in the United Kingdom. Does thrombophilia testing help type allergic skin reactions due to administration of LMWH occur in the clinical management of patients? International consensus with nadroparin in the ALIFE study.

However purchase sinequan 75mg with mastercard anxiety symptoms vision problems, accrual was stopped after Data Safety and age discount sinequan 25mg line anxiety symptoms in men, 2-year OS rates were 7% and 22% in those with MK( )-AML Monitoring Plan analysis suggested a benefit from high-dose and MK( )-AML, respectively (P. New models for risk assessment before allogeneic HCT29 432 patients who received HCT; of those, 14% of patients were should prove very useful in informing future trials comparing MK( )-AML and 21% were 60 years of age. The 4-year OS rate nonmyeloablative and RIC for patients 65 years of age. In the setting The majority of patients will have a parent, sibling, or child that is of RIC-HCT, however, grafts from HLA-matched unrelated donors HLA-haploidentical matched. Haploidentical transplantations have and HLA-identical siblings resulted, on average, in comparable been facilitated by using T-cell-depleted grafts to ameliorate risks of GVHD with acceptable rates of engraftment and disease control. For example, a study analyzing data from 221 and 184 recipients of HLA-matched related and Another approach is the use of 2 Gy TBI and fludarabine, 150 mg/m2, in addition to cyclophosphamide administered before to unrelated donor grafts, respectively, after nonmyeloablative condi- tioning found no significant differences in NRM (HR 0. Results have been However, another study in 433 patients receiving fludarabine and IV encouraging with regard to NRM but at the expense of weakened GVT effects. Stem cells sources other than HLA-matched sibling or matched Donor age unrelated donors are required for 40% of Caucasians and 80% of The effect of donor age on the quality and quantity of transplanted ethnic minorities32 or for those requiring urgent HCTs because of a hematopoietic cells and, therefore, the resulting outcome is an high risk for progression or relapse. Advanced donor age was shown to increase risks for GVHD43 and shorter survival44 when high-dose regimens source is the HLA-mismatched donor. Historically, this graft type has been associated with higher risks for GVHD and increased risks were used. However, results are different when RIC regimens are for NRM and overall mortality compared with HLA-matched grafts. For example, among 125 recipients of Despite the use of nonmyeloablative regimens followed by 1 nonmyeloablative conditioning, increasing donor age was only antigen 1 allele HLA class I mismatch or 2 HLA class I allele associated with lower day 28 donor T-cell chimerism (P. Grafts from younger unrelated donors evaluated outcomes in 1933 unrelated donor recipients, of whom conferred higher risks for grades II-IV acute GVHD (HR 1. High-resolution typing for HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, benefit for older sibling donors was limited to those with perfor- HLA-DRB1, HLA-DQA1, and HLA-DQB1 was done for all mance status (PS) of 90%–100%. Results suggest that donor age 34 should not be factored into risk assessment. In adjusted comparisons, 8/8 matching for HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, and HLA-DRB1 alleles was associated with better OS at 1 year compared with any 7/8 HLA-matched pairs Other factors (56% vs 47%). HLA-C antigen mismatches (n 189) predicted Grafts from a female donor to a male recipient carry higher risks increased risk for overall mortality [relative risk (RR) 1. No other statistically significant ing KIR “killing immunoglobulin-like receptors” are associated with better OS. Another study Patient-specific factors (Table 2) from the National Marrow Donor Program confirmed worse OS for Age a single mismatch compared with 8/8 match, but highlighted higher In the setting of high-dose conditioning before allogeneic HCT for risks for mortality with HLA-A and HLA-DRB1 mismatches young patients, age 40 years was shown to be associated with compared with HLA-A and HLA-C. The European Group for Blood mismatch on hematopoietic recovery and OS after UCB-HCT can and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) found similar 4-year rates of be mitigated by increasing the cell dose of the infused UCB. Results of reported that 2-year rates of OS were 44%, 50%, 34%, and 36% in UCB HCT after RIC suggested reduced incidences of chronic patients 40-54, 55-59, 60-64, or 65 years, respectively. Moreover, median ages in these studies of 46%, 39%, 36%, and 37% in patients 60-64 (n 1958), 65-69 ranged between 51 and 60 years. Outcomes of patients of 60 y or older after allogeneic HCT as stratified by patient-specific variables Outcomes at 2 y Outcomes at 5 y Other outcomes Categories/ III-IV acute Post-GVHD Risk variable stratifications NRM, % OS, % NRM, % OS, % GVHD, % 2-y survival Age, y: WP,SE (Marcelo 60-65 24-32 34-50 27 48 15 – Pasquini, personal 66-70 23-34 36-44 26 38 12 – communication)50,51 70-75 22-NA 36-44 31 27 9 – 75 – 37 – – – – HCT-CI scores: SP,SE51,55,56,61 0 12-15 54-69 18 50 9 68 1-2 18-22 49-59 26 39 14 51 3 30-31 39-49 34 26 23 28 5 40-42 31-32 – – 28 22 6 – – – – 7 – – – – 8 – – – – KPS: WP,WE65 80% 20 56 – – – – 80% 28 44 – – – – Thecriterionforstrongversusweakpredictionwasmagnitudeofdiscriminativecapacityofthevariable,whereasdeterminationofstrongversusweakevidencewasbasedon theamountofdataavailable. The HCT-CI scores were found in several studies to Transplant Research, personal communication). A recent study stratify patients into multiple risk groups for prediction of NRM and presented data from 372 patients prospectively enrolled into 21 OS. It has been validated in 2 large rates of DFS and OS were 32% and 35%, respectively. There were prospective studies in Italy and the United States. As a comorbidities for NRM,51 and comorbidities and PS for OS. Conclusions must be tempered because the number of patients 70 years of age in the various datasets is limited. The referral rate of older patients to PS allogeneic HCT is also limited,52 raising questions about the PS scales have the advantages of simplicity and ease of use. They applicability of reported results to all older AML patients.